
We have designed a number of robots using the EyeBot Controller, precision DC motors and various sensors. For details see the book "Embedded Robotics".
See driving robot videos.

Eve (EyeBot Vehicle) was the first driving robot we build around a specialized EyeBot controller and a QuickCam camera system. This robot has the standard top part of the EyeBot M1 controller, but a modified bottom board that matches the outline of the physical robot. We later discarded this technique for a standard controller (M3) that is identical for all robot vehicles.
Eve is equipped with:

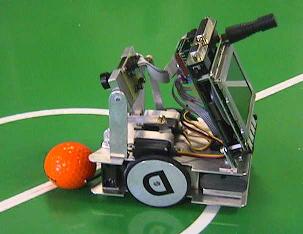
Our next driving robot designs were a number of variations for the CIIPS Glory Robot Soccer Team. These robots had to be somewhat smaller than Eve, in order to qualify for the RoboCup competition, where we entered the 1998 regional contest in Singapore. The original CIIPS Glory player was equipped with a Color QuickCam camera, which was replaced in later versions by our own EyeCam design. CIIPS Glory robots have competed in a number of RoboCup and FIRA World Cup robot soccer events.
We used two servos in addition to the two DC driving motors. These were used for:
The original camera movement was a tilt action, which allowed us to keep the ball in the (relatively narrow) field of view, when closing in on the ball. We changed this on later robots in favour of a panning movement, which allows faster tracking of a moving ball without having to move the whole robot, or a combination of both.
The goal keepers were a variation of the field player design. Since they needed to move primarily sideways instead of forward/backward, re mounted the goal keeper's top plate at a 90 degree angle to the bottom plate and equipped it with a larger ball kicking plate, as lined out in the RoboCup rules.


LabBot is a more robust vehicle we designed to survive the harsh environment of a daily student lab. We use these robots for the course "Embedded Systems", but they have also competed in several FIRA RoboSot competitions. FIRA, unlike RoboCup, has established a robot soccer league for autonomous small-sized robots, i.e. with local vision capability.
The lab robots are equipped with the same EyeBot controller, EyeCam camera and infrared sensors as the previous robots. However, they also have an electromagnet, which can be switched via a digital output. This enables them to transport tin cans that they can locate using their on-board vision system.
TPU 0 right motor speed TPU 1 left motor speed TPU 2-3 left shaft encoder TPU 4-5 right shaft encoder TPU 2-13 servo channels (4 overlapping) TPU 14 PSD TPU 15 audio out ------- DO 0-1 left motor direction (A) DO 2-3 right motor direction (B) DO 4 PSD control line DO 5-7 free ------- DI 0-5 PSD infrared sensor DI 6-7 free (e.g. bumper) ------ AD 0 microphone AD 1 battery level AD 2-7 free